
Introduction
Statistical arbitrage, often called “stat arb,” is like finding hidden patterns in market prices. While traditional traders rely on charts and news, stat arb traders use complex mathematical models to spot market inefficiencies and profit from them. Let’s explore how this fascinating strategy works and why it’s become a cornerstone of quantitative trading.
Understanding Statistical Arbitrage
What is Stat Arb?
Statistical arbitrage is a quantitative trading strategy that:
- Identifies pricing inefficiencies using statistical methods
- Takes offsetting positions in related securities
- Aims to profit regardless of market direction
- Relies heavily on automation and algorithms
For a deeper understanding of quantitative trading strategies, visit the CFA Institute’s guide to systematic trading.
Key Components of Stat Arb
- Statistical Analysis
- Mean reversion studies
- Correlation analysis
- Price deviation measurements
- Risk Management
- Position sizing
- Stop-loss parameters
- Portfolio diversification
- Execution Infrastructure
- High-speed trading systems
- Low-latency connections
- Advanced order management
Understanding Stat Arb Through Visual Examples
While statistical arbitrage can seem complex on paper, seeing it explained visually can help clarify the concept. The following video provides an excellent breakdown of how stat arb works in practice. It uses clear examples and visual aids to demonstrate the key principles we’ve discussed above, making it easier to grasp this sophisticated trading strategy.
Watch this comprehensive explanation of statistical arbitrage:
This video helps illustrate:
- The basic mechanics of a stat arb trade
- How traders identify statistical patterns
- Real-world examples of price divergence
- Common pitfalls to avoid when implementing stat arb strategies
After watching the video, you’ll have a better understanding of how quantitative traders apply these concepts in real market conditions.
How Statistical Arbitrage Works
The Basic Process
- Identify Relationships: Find securities that historically move together
- Detect Divergence: Spot when these relationships temporarily break down
- Execute Trades: Take opposing positions in the related securities
- Wait for Convergence: Profit when prices return to their statistical norm
Common Stat Arb Strategies
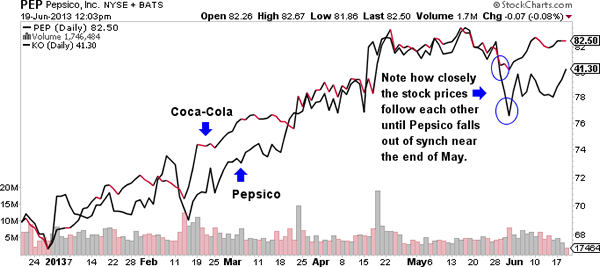
- Pairs Trading
- Long-short positions in correlated stocks
- Example: Coca-Cola vs. Pepsi
- Index Arbitrage
- Trading index futures against constituent stocks
- Example: S&P 500 futures vs. underlying stocks
- ETF Arbitrage
- Exploiting price differences between ETFs and their components
- Example: Gold ETF vs. gold mining stocks
Leading Firms in Statistical Arbitrage
Renaissance Technologies
- Founded by mathematician James Simons
- Known for the Medallion Fund
- Notable Achievement: Generated $1+ billion from S&P 500 futures arbitrage
Two Sigma
- Combines traditional stat arb with machine learning
- Manages over $60 billion in assets
- Famous for Treasury futures arbitrage success
AQR Capital Management
- Founded by Cliff Asness
- Pioneered risk parity strategies
- Notable Success: $200+ million corporate bond arbitrage
For more on quantitative hedge funds, read Institutional Investor’s guide to quant funds.
Advantages and Challenges of Stat Arb
Advantages:
- Market-neutral strategy
- Scalable across multiple markets
- Based on mathematical principles
- Can generate consistent returns
Challenges:
- Requires substantial technological infrastructure
- High competition reduces opportunities
- Strategy capacity constraints
- Model risk and breakdown potential
Technology and Infrastructure Requirements
Hardware Needs:
- High-performance computing clusters
- Low-latency network connections
- Redundant systems for reliability
Software Requirements:
- Advanced statistical packages
- Real-time data processing capabilities
- Risk management systems
- Order execution platforms
Risk Management in Stat Arb
Key Risk Factors:
- Model Risk: When statistical relationships break down
- Liquidity Risk: Unable to exit positions efficiently
- Technical Risk: System failures or glitches
- Regulatory Risk: Changes in trading rules or regulations
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
- Regular model validation
- Position size limits
- Stop-loss protocols
- Diversification across strategies
FAQs
- Q: What’s the minimum capital needed for stat arb?
A: Due to infrastructure requirements and execution costs, successful stat arb typically requires institutional-scale capital ($10M+). - Q: Can individual investors implement stat arb strategies?
A: While challenging, individuals can use simplified versions through retail platforms, but with limited effectiveness. - Q: How has machine learning impacted stat arb?
A: ML has enhanced pattern recognition and strategy development, leading to more sophisticated approaches. - Q: What’s the typical holding period for stat arb trades?
A: It varies from minutes to weeks, depending on the specific strategy and market conditions. - Q: How do stat arb firms maintain their edge?
A: Through continuous research, technology investment, and strategy evolution.
Future of Statistical Arbitrage
As markets evolve, stat arb continues to adapt:
- AI Integration: Machine learning enhancing traditional models
- Alternative Data: Incorporating new data sources
- Market Evolution: Adapting to changing market structures
- Regulatory Changes: Responding to new trading rules

Conclusion
Statistical arbitrage represents the intersection of mathematics, technology, and finance. While not accessible to all investors, understanding stat arb provides insights into how quantitative traders approach markets. As technology advances and markets evolve, stat arb strategies continue to adapt and find new opportunities.
For those interested in quantitative trading, stat arb offers valuable lessons about market efficiency, risk management, and the importance of systematic approaches to trading.
Want to learn more about quantitative trading? Start by studying basic statistical concepts and market relationships. Consider exploring platforms that offer paper trading to practice identifying statistical patterns without risking capital. For serious practitioners, investigate professional certifications in quantitative finance.