Introduction
Geo-location data sets are transforming industries by providing precise information on the geographical location of objects or events, ranging from mobile devices to retail store visits. This powerful tool offers unprecedented insights into consumer behavior, traffic patterns, and logistical operations. This article discusses the significance of geo-location data sets, their sources, benefits, challenges, and their transformative impact on various sectors.
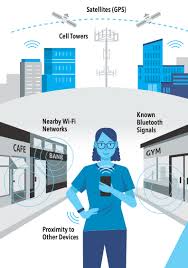
What are Geo-Location Data Sets?
Geo-location data refers to the geographical positioning information collected from various devices and technologies, indicating where a device or individual is located at a given time. This data is typically gathered via GPS, Wi-Fi, cell towers, and other location-sensing technologies in smartphones and other devices.
Key Sources of Geo-Location Data
- GPS-Enabled Devices: Data collected from smartphones, cars, and other GPS-equipped devices.
- Social Media: Location tags in social media posts and check-ins.
- Wi-Fi and Beacons: Location data gathered from Wi-Fi networks and Bluetooth beacons in stores or urban areas.
- Geotagged Media: Photos and videos tagged with geographical information.
Benefits of Geo-Location Data Sets
Enhanced Consumer Insights
Geo-location data provides detailed insights into consumer movements and behaviors, allowing businesses to tailor marketing strategies and product offerings.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Logistics companies use geo-location data to optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and improve delivery times.
Strategic Decision Making
Businesses use this data to make informed decisions about where to open new stores, how to manage inventory, and ways to enhance customer experiences.
Real-Time Data Application
Geo-location data is essential for real-time applications, such as ride-sharing and mobile advertising, providing immediate contextual relevance.
Challenges in Utilizing Geo-Location Data Sets
Privacy Concerns
Handling geo-location data requires strict compliance with privacy laws and regulations, as it involves sensitive information about individuals’ movements.
Data Accuracy and Integrity
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of geo-location data is crucial, as errors can lead to misguided decisions and operational inefficiencies.
Data Volume and Complexity
Processing and analyzing large volumes of geo-location data require advanced data management and analytical capabilities.
Case Studies
Retail companies analyze foot traffic data to understand peak times and shopper behaviors, enhancing store layouts and promotional strategies. Urban planners use geo-location data to analyze traffic patterns and optimize public transportation routes and schedules.
Future of Geo-Location Data Sets
The increasing ubiquity of connected devices and the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) are likely to drive the growth and application of geo-location data. Innovations in data processing and artificial intelligence will further enhance the ability to derive actionable insights from this data.
Extract Alpha
Extract Alpha datasets and signals are used by hedge funds and asset management firms managing more than $1.5 trillion in assets in the U.S., EMEA, and the Asia Pacific. We work with quants, data specialists, and asset managers across the financial services industry.
Conclusion
Geo-location data sets are vital tools in understanding and influencing spatial dynamics in various fields. As technology advances, the potential for geo-location data to inform and transform decisions continues to expand, offering significant opportunities for businesses and public agencies alike.
Commonly Asked Questions by Data Analysts
- How can businesses start integrating geo-location data into their existing data systems?
- Businesses can begin by partnering with geo-location data providers and integrating this data with existing analytics platforms using APIs.
- What are the best practices for ensuring the privacy of individuals in geo-location data analysis?
- Implementing data anonymization, ensuring data minimization, and maintaining transparency with users about how their data is used are crucial practices.
- Can geo-location data be used to improve online and offline customer experiences?
- Absolutely, businesses can use geo-location data to offer personalized online content and optimize physical store experiences based on consumer location patterns.
- What tools are necessary for processing and analyzing geo-location data?
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS), advanced data analytics platforms, and location intelligence software are essential for processing and analyzing geo-location data effectively.
- How do advancements in technology affect the use of geo-location data?
- Technological advancements, especially in mobile technology and IoT, enhance the accuracy and availability of geo-location data, expanding its use cases and value.