Backtesting is a vital process in financial analysis that helps investors evaluate the accuracy and effectiveness of their investment strategies. It is a statistical method that tests an investment strategy by applying it to historical data to determine how it would have performed in the past.
Here is a short summary on backtesting:
Backtesting evaluates trading strategies using historical data, assessing their viability and risks for informed investment decisions.
Lazy to read? This video does a great job explaining how to backtest properly
What Is Backtesting?
Backtesting is the general method for seeing how well a strategy or model would have done ex-post. Backtesting assesses the viability of a trading strategy by discovering how it would play out using historical data. If backtesting works, traders and analysts may have the confidence to employ it going forward.
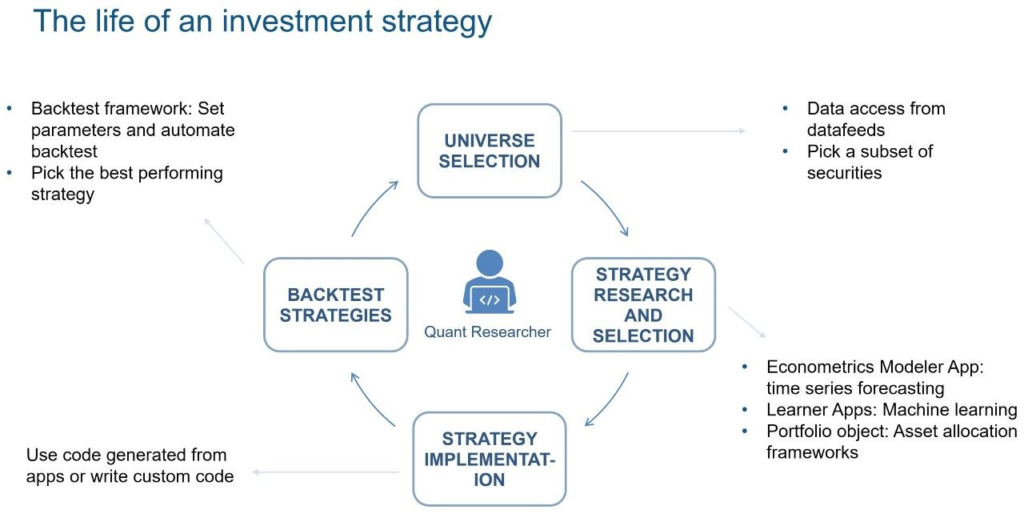
Importance
Backtesting is an essential step in the investment process since it provides investors with insights into how their investment strategies would have performed in the past. By analyzing historical data, investors can evaluate how their strategies have performed in different market conditions, identify strengths and weaknesses, and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Backtesting serves as a valuable tool in deciphering historical market behaviors, offering statistical insights into a trading system’s performance. This process plays a crucial role in measuring risk and potential returns, paving the way for more effective trading decisions. By utilizing backtesting, traders have the opportunity to evaluate and compare various strategies without immediately committing their capital.
When conducted meticulously, and if it yields encouraging outcomes, backtesting can affirm the foundational robustness of a trading strategy. This reassurance empowers traders to proceed with confidence, as the strategy demonstrates a high likelihood of success in real market conditions.
Conversely, a thorough backtesting process that does not meet expected results is equally informative. It signals traders to reconsider their approach, inviting them to refine or possibly discard the strategy under review. This critical feedback loop ensures that traders are more informed and cautious in their strategy selection, ultimately aiming to enhance their chances of successful trading.
How Backtesting Works
Backtesting allows a trader to simulate a trading strategy using historical data to generate results and analyze risk and profitability before risking any actual capital.
Works by applying an investment strategy to historical data to determine how it would have performed in the past. The process involves selecting a time period, defining the investment strategy, and applying it to the historical data. The results of the backtesting process are then analyzed to evaluate the effectiveness of the investment strategy.
To delve deeper into how backtesting operates, it is crucial to understand that it allows traders to simulate a chosen strategy using historical data, offering a simulated environment to analyze risk and profitability without risking actual capital. However, the effectiveness of backtesting is contingent on the selected time period, the definition of the investment strategy, and the meticulous application of the strategy to historical data.
Understanding Backtesting:
Exploring Backtesting in Trading Backtesting enables traders to test their trading strategies using past market data, assessing both risk and potential profitability before investing real money.
When backtesting yields favorable outcomes, it reassures traders that their strategy has a solid foundation and stands a good chance of being profitable in real-world trading. On the other hand, if the backtesting results are less than ideal, it prompts traders to modify or abandon the strategy.
Complex trading strategies, particularly those used in automated trading systems, depend heavily on backtesting for validation, as their intricacies make them difficult to assess by other means. Any tradable idea, if it can be quantified, is eligible for backtesting. Traders and investors might sometimes require the skills of a proficient programmer to transform their ideas into a format suitable for backtesting. This usually involves programming the strategy into the specific language used by the trading platform.
Programmers can add customizable input options for the trader to adjust the strategy. For instance, in a simple moving average (SMA) crossover system, a trader can input different lengths for the two moving averages used. The trader can then backtest these variations to find out which combination of moving average lengths would have been most effective using historical data.
Optimizing Backtesting for Reliable Results
A thorough backtesting process should ideally select data from a period that accurately represents various market conditions. This approach helps in determining if the backtest results are consistently reliable or merely a stroke of luck.
For a backtest to be effective, it’s crucial to use a dataset that encompasses a wide range of stocks, including those from companies that failed, were acquired, or ceased operations. Limiting the dataset to currently successful stocks could lead to an overestimation of potential returns, as it excludes the full spectrum of possible outcomes. Websites like Investopedia and QuantConnect offer insights on selecting appropriate datasets for backtesting.
It’s also important to factor in all trading costs in the backtest, no matter how small they may seem. Over time, these costs can significantly impact the perceived profitability of a strategy. Resources like BabyPips and Quantpedia provide information on how to accurately include trading costs in backtesting scenarios.
Additionally, conducting out-of-sample and forward performance testing can give further evidence of a system’s efficacy. These tests can reveal the true potential of a trading strategy before real money is involved. A consistent performance across backtesting, out-of-sample, and forward tests is a strong indicator of a strategy’s viability. Websites like QuantStart and Elite Trader offer guidance on implementing these additional testing methods effectively.
In summary, for backtesting to be truly beneficial, it must encompass a comprehensive and realistic approach, considering varied data, all trading costs, and additional testing phases.
Navigating the Challenges of Backtesting
Effective backtesting requires traders to approach strategy development and testing with integrity and an objective mindset. It’s essential to create trading strategies independently from the data used in backtesting to avoid biased results. This objective approach can be challenging, as traders often rely on historical data to shape their strategies. To ensure accuracy, it’s crucial to test these strategies with different datasets than those used during their development. This prevents the common pitfall of backtests showing overly optimistic results that don’t translate into real-world success.
Additionally, traders should be wary of data dredging. This practice involves testing numerous hypothetical strategies against the same dataset, which can misleadingly indicate success due to random chance rather than genuine strategy effectiveness. Many strategies might appear successful over a specific period by chance, but they may not hold up in actual market conditions.
A constructive approach to mitigate these issues is to apply a two-phase testing process. First, validate the strategy with an in-sample (relevant time period) dataset, and then conduct a backtest using a different, out-of-sample dataset. Consistency in performance across both in-sample and out-of-sample backtests can significantly enhance the credibility of the strategy’s effectiveness. This method provides a more robust and reliable evaluation of a trading strategy’s potential success.
Examples Of Backtesting
In the realm of finance, backtesting is a pivotal tool that allows traders and analysts to evaluate investment strategies using historical data. A visual representation captures this process, showing a financial analyst at work, surrounded by screens displaying stock market charts and data, emblematic of the detailed analysis inherent in backtesting. Through examples, such as an intraday trader testing a 30-day low stock purchase strategy and a team of traders exploring various methods for balanced returns, we see backtesting’s crucial role in refining and developing effective investment strategies, demonstrating its indispensable value in financial decision-making.

Example 1: Intraday Trading Strategy Evaluation
A scenario involves an intraday trader at a major investment firm. The firm’s objective is to evaluate a new trading strategy: purchasing stocks at their 30-day low point to see if it leads to a positive return. The trader gathers extensive historical data on numerous stocks and applies this strategy retrospectively.
Upon analysis, the strategy outperforms the firm’s existing approach by an average of 60 points. This significant improvement leads the firm to adopt this strategy for future trades, with plans to adjust it as needed based on ongoing return on investment assessments.
Example 2: Agency Team’s Diverse Strategy Analysis
In this case, a team of traders at an agency embarks on a backtesting project. Their aim is to find an optimal strategy that balances medium risk with high returns, employing various underutilized investment tactics. They meticulously analyze five years of market data, incorporating technical analysis, financial reports, and yearly market sentiment.
Their exhaustive testing reveals that several strategies result in negative returns. However, perseverance pays off when they discover a method yielding a 50-point profit. This finding is then presented to the agency’s lead investor for further decision-making and potential implementation.
These examples illustrate how backtesting is utilized in the financial world to refine and develop effective investment strategies.
To create a comprehensive table featuring different types of alternative data, their typical costs, and usefulness in investing, I’ll outline a format and then populate it with relevant information.
Benefits and added insights
provides investors with several benefits, including:
- Identifying potential risks and weaknesses of a strategy before investing real money
- Improving the accuracy of investment decisions by providing insights into how a strategy would have performed in different market conditions
- Reducing the risk of investment losses by identifying potential pitfalls in the investment strategy before implementing it
- Enhancing the overall performance of the investment portfolio by enabling investors to fine-tune their investment strategies
While the benefits of backtesting are extensive, it’s essential to highlight its role in identifying potential risks and weaknesses before actual capital is invested. Furthermore, the accuracy of investment decisions is significantly improved by gaining insights into how a strategy would have performed in various market conditions. Investors can leverage this information to fine-tune their strategies, ultimately enhancing the overall performance of their investment portfolios.
What Are the Main Points to Consider in Backtesting?
There are three major points to consider when conducting a backtest. Backtesting typically requires a specific trading strategy or idea, historical data, and measures on returns.
Expanding on the three major points to consider during a backtest, the significance of the trading strategy cannot be overstated. The meticulous selection of a strategy determines the type and duration of data collected, influencing the robustness of the backtesting process.
Trading Strategy
Picking a trading strategy is the first step in backtesting. This will determine what type of data will be collected and for how long.
Data
Collecting accurate data is important in backtesting. Data should be free of errors, and results from backtesting will depend on the type of historical data selected.
Key Performance Indicators
Key performance indicators are used to determine whether the performance of a trading strategy results in a profit or loss. Some of the common KPIs include total return, annualized return, and the Sharpe ratio.
To further bolster the evaluation process, the incorporation of key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential. These metrics, such as total return, annualized return, and the Sharpe ratio, play a pivotal role in determining the profitability and effectiveness of a trading strategy.
Limitations of Backtesting
Although it is a useful tool, it is not without limitations. One of the most significant limitations is that it is based on historical data, which may not accurately reflect future market conditions. Additionally, backtesting assumes that investors would have acted consistently in the past, which may not always be the case.
While acknowledging the importance of backtesting, it’s crucial to recognize its limitations. Historical data, upon which backtesting relies, may not always accurately reflect future market conditions. Additionally, traders must guard against pitfalls such as bias, data dredging, and cherry-picking strategies based on historical data.
Some Pitfalls of Backtesting
For backtesting to provide meaningful results, traders must develop their strategies and test them in good faith, avoiding bias as much as possible. That means the strategy should be developed without relying on the data used in backtesting.
That’s harder than it seems. Traders generally build strategies based on historical data. They must be strict about testing with different data sets from those they train their models on. Otherwise, the backtest will produce glowing results that mean nothing.
Similarly, traders must avoid data dredging, in which they test a wide range of hypothetical strategies against the same set of data, which will also produce successes that fail in real-time markets because there are many invalid strategies that would beat the market over a specific time period by chance.
One way to compensate for the tendency to data dredge or cherry-pick is to use a strategy that succeeds in the relevant, or in-sample, time period and backtest it with data from a different, or out-of-sample, time period. If in-sample and out-of-sample backtests yield similar results, then they are more likely to be proved valid.
FAQ: Understanding and Performing Backtesting in Trading
How do you perform backtesting?
Backtesting involves simulating a trading strategy using historical market data to evaluate its performance. This process typically includes selecting a time period, obtaining relevant historical data, defining specific rules for your trading strategy, and then applying these rules against the data to observe how the strategy would have performed. Don’t forget to include transaction costs and ensure the data is free of biases. For a comprehensive guide on backtesting, visit Investopedia: Investopedia Backtesting Guide or QuantInsti: QuantInsti Backtesting Resources.
What is an example of a backtest strategy?
A common example is the Moving Average Crossover strategy. This involves using two moving averages of a security’s price – a short-term and a long-term average. A trade signal is generated when these averages cross. For detailed examples and explanations, check out DailyFX: DailyFX Moving Average Strategies.
What is backtesting a model?
Backtesting a model involves testing a predictive model or trading algorithm using historical data to evaluate its accuracy in predicting future events. This is crucial in financial markets for validating trading decisions. For more in-depth information, consider exploring quantitative analysis websites and financial modeling courses.
Where can I backtest my strategy?
You can backtest on platforms like TradingView (TradingView), MetaTrader (MetaTrader), QuantConnect (QuantConnect), and NinjaTrader (NinjaTrader). Each platform offers unique features suitable for different levels of trading experience.
How do I backtest using TradingView?
On TradingView, use the Pine Script language to create custom trading strategy scripts for backtesting. After scripting your strategy, apply it to historical data on the platform. TradingView’s forums and Pine Script documentation provide resources for scripting and implementation: TradingView Pine Script Documentation.
How can I backtest forex?
Backtesting a forex strategy requires historical forex market data and clear trade entry and exit rules. Platforms like MetaTrader are popular for forex backtesting, offering tools for strategy development and testing. For tutorials on forex backtesting, visit BabyPips: BabyPips Forex Backtesting.
These links offer valuable insights and tools for anyone interested in learning more about backtesting and its application in trading strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, backtesting is a crucial tool for investors seeking to evaluate the effectiveness of their investment strategies. By analyzing historical data, investors can identify potential risks and weaknesses, fine-tune their strategies, and make better investment decisions. As such, investors should always include backtesting as a critical step in their investment process.